This series of walkthroughs aims to help out complete beginners with finishing the Pre Security Path on the TryHackMe (thm)1 website.
It is based on the learning content provided in the Extending Your Network room.
Task 1 - Introduction to Port Forwarding
Check out how port forwarding works, and why it is so essential for network communications.
Question 1: What is the name of the device that is used to configure port forwarding?
router
Task 2 - Firewalls 101
Read about the differences between a stateful and a stateless firewall.
Question 1: What layers of the OSI model do firewalls operate at?
Layer 3,Layer 4
Question 2: What category of firewall inspects the entire connection?
stateful
Question 3: What category of firewall inspects individual packets?
stateless
Task 3 - Practical - Firewall
The flag will present itself, after you successfully, and correctly configured the firewall found on the attached static site. Your goal is to prevent a device from overloading by adding the appropriate firewall rule to the router in the middle.
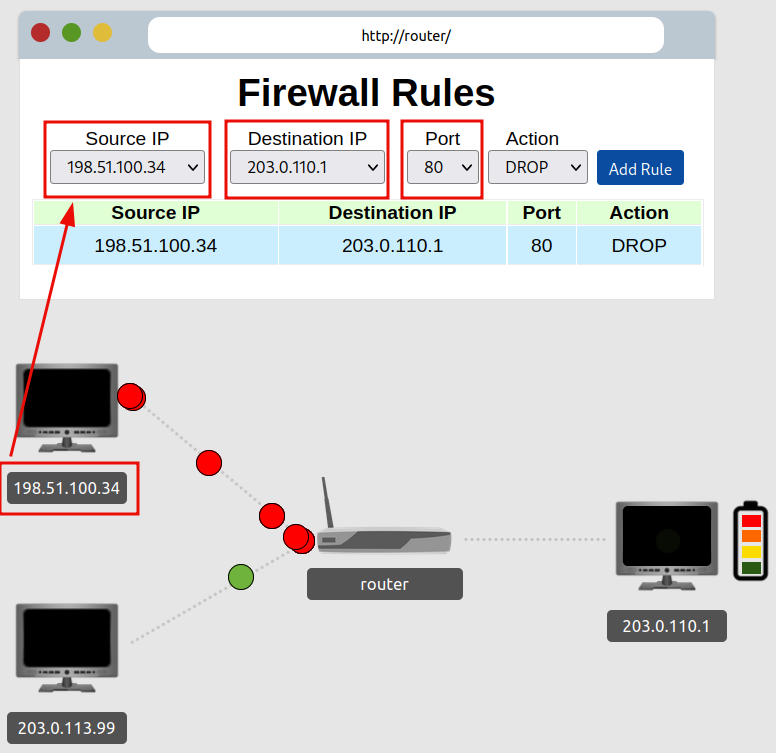
Configure the router to drop all packets accessing our web server (port 80) from the attacker’s machine. (IP - 203.0.110.1)
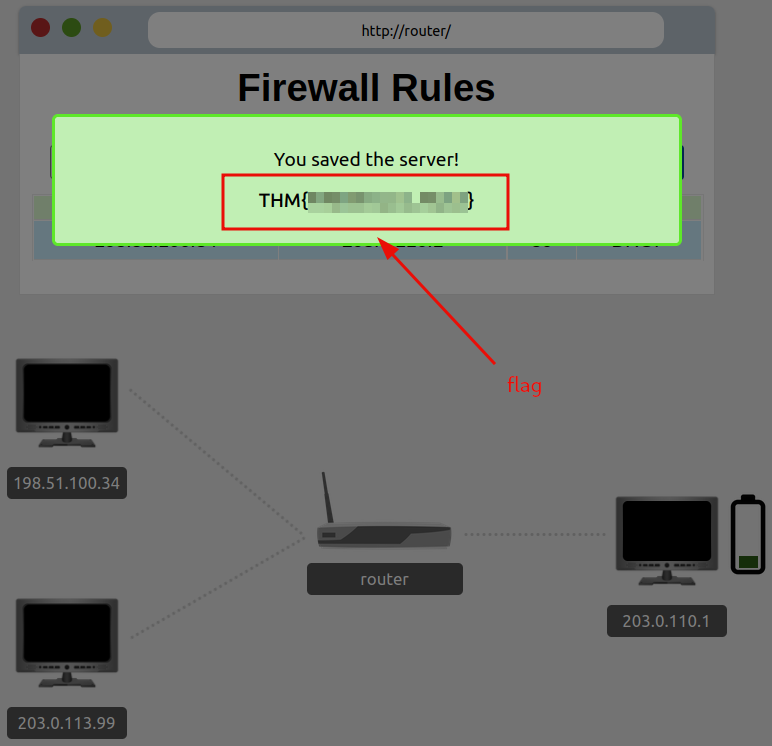
Question 1: What is the flag?
flag
Task 4 - VPN Basics
Make yourself comfortable with VPN technology, and check out the advantages it can provide. Read about it’s various technologies before moving on to the next task.
Question 1: What VPN technology only encrypts & provides the authentication of data?
PPP
Question 2: What VPN technology uses the IP framework?
IPSec
Task 5 - LAN Networking Devices
The different LAN networking devices like routers and switches are introduced here.
Question 1: What is the verb for the action that a router does?
routing
Question 2: What are the two different layers of switches? Separate these by a comma I.e.: LayerX,LayerY
Layer2,Layer3
Task 6 - Practical - Network Simulator
The network simulator attached to this task will break down the communication between two points, and displays it graphically. Play around a bit with it, and get a better understanding how exactly the communication happens.
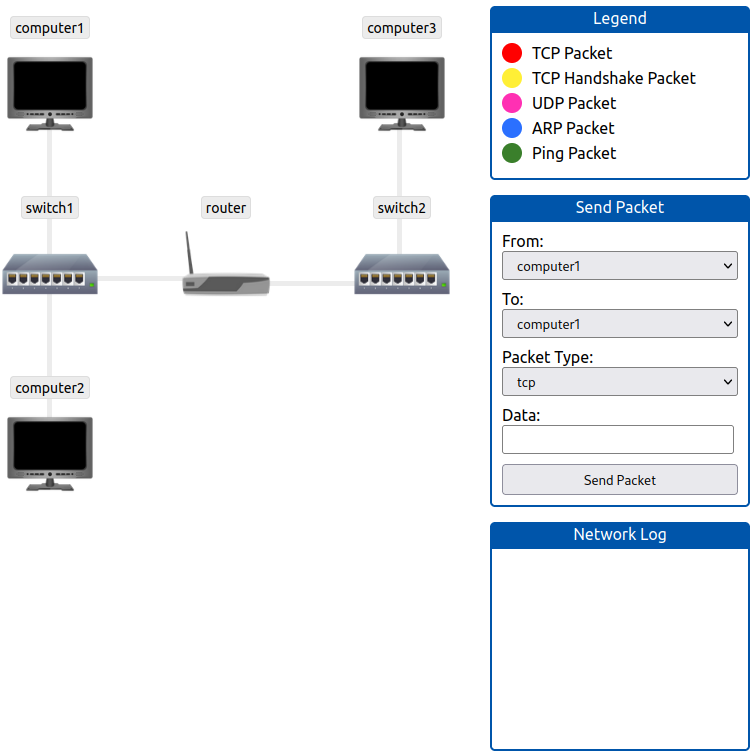
Send a TCP packet from computer1 to computer3 with the help of the switches and the router on the path connecting them.
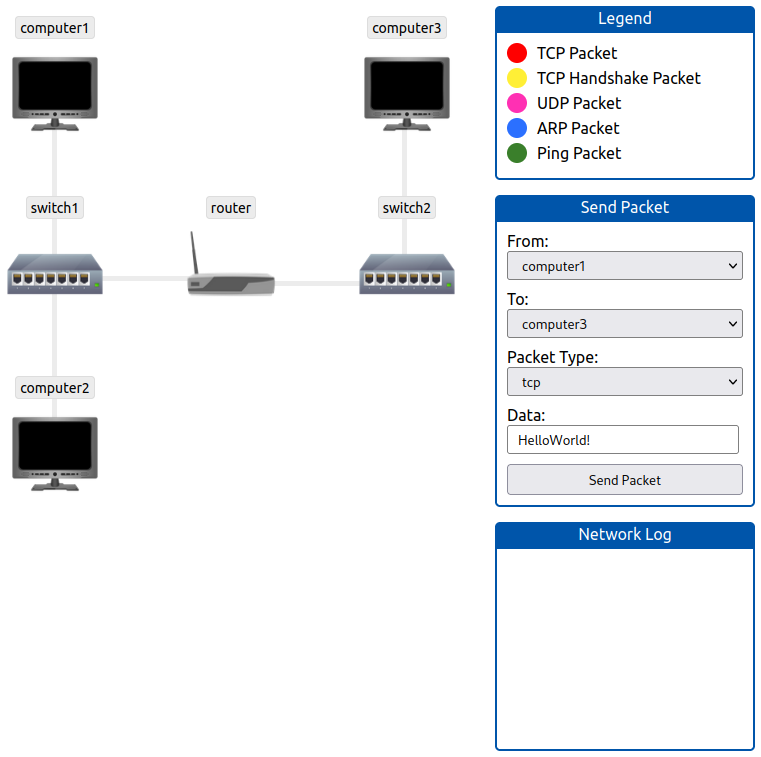
After our packet was received on computer3, a pop-up window provides us with the flag.

Check out the network log that was created after sending a single TCP packet from computer1 to computer3.
| Step | Connection type | Network log |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HANDSHAKE | Starting TCP/IP Handshake between computer1 and computer3 |
| 2 | HANDSHAKE | Sending SYN Packet from computer1 to computer3 |
| 3 | ROUTING | computer1 says computer3 is not on my local network sending to gateway: router |
| 4 | ARP REQUEST | Who has router tell computer1 |
| 5 | ARP RESPONSE | Hey computer1, I am router |
| 6 | ARP REQUEST | Who has computer3 tell router |
| 7 | ARP RESPONSE | Hey router, I am computer3 |
| 8 | HANDSHAKE | computer3 received SYN Packet from computer1, sending SYN/ACK Packet to computer1 |
| 9 | HANDSHAKE | computer1 received SYN/ACK Packet from computer3, sending ACK packet to computer3 |
| 10 | HANDSHAKE | computer3 received ACK packet from computer1, Handshake Complete |
| 11 | TCP | Sending TCP packet from computer1 to computer3 |
| 12 | TCP | computer3 received TCP Packet from computer1, sending ACK Packet to computer1 |
With this, we arrived at the end of this room. This also marks the completion of the Network Fundamentals module.
Question 1: What is the flag from the network simulator?
flag
Question 2: How many HANDSHAKE entries are there in the Network Log?
5
thm - shorthand for TryHackMe from now on ↩︎